INTRODUCTION TO GST AUDIT
While the GST regime emphasizes self-assessment processes, the complexities involved in it make one wary.
At this juncture, it is clear that the GST law is not presently simple enough for an assessee to compute his total and taxable turnovers and duly report the same.
Thus, in order to ensure effective compliance with the various GST provisions and to ensure performance of audits in a systematic, transparent and fair manner, audit provisions have been incorporated under the GST Acts/ Rules.
Definition of the term “Audit”
Section 2(13) of the CGST Act/SGST Act provides
“Audit” means the examination of records, returns and other documents maintained or furnished by the registered person under the GST Acts or the rules made there under or under any other law for the time being in force to verify the correctness of turnover declared, taxes paid, refund claimed and input tax credit availed, and to assess his compliance with the provisions of the GST Acts or the rules made there under.
Audit under GST
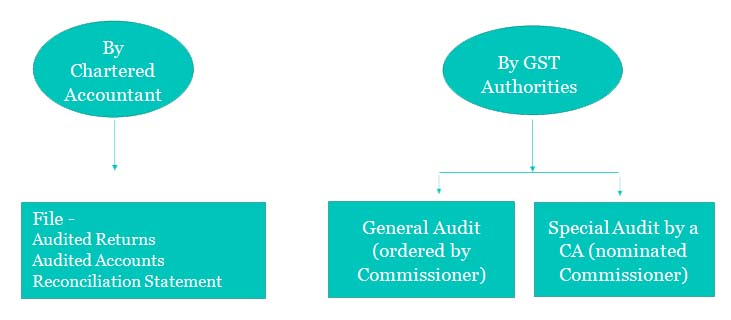
Audit by a Chartered Accountant
Section 35(5) of the CGST Act/ SGST Act read with Rule 80(3) of the CGST/SGST Rules, 2017
- Registered person having turnover during a financial year s. 2 Crore or more shall get his accounts audited by a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant
- The term “aggregate turnover” has been defined as under vide Section 2(6) of the CGST Act/SGST Act:
“Aggregate Turnover” means the aggregate value of all taxable supplies (excluding the value of inward supplies on which tax is payable by a person on reverse charge basis), exempt supplies, exports of goods or services or both and inter-State supplies of persons having the same Permanent Account Number, to be computed on all India basis but excludes central tax, State tax, Union territory tax, integrated tax and cess
|
|
Inclusions
An exhaustive definition under Section 2(6) of the CGST Act/SGST Act
Alcoholic Liquor for Human Consumption and five specified Petroleum Products i.e. Petroleum Crude, Motor Spirit (Petrol), High Speed Diesel [HSD], Natural Gas and Aviation Turbine Fuel [ATF]
|
However, certain Exclusions shall be made while computing the Value of Aggregate Turnover
 |
i) Value of Inward supplies on which tax is payable by a person on Reverse Charge basis.
Examples of supplies subject to Reverse Charge are- Services provided by way of Sponsorship to any Body Corporate or Partnership Firm, Services supplied by a Director of a Company or Body Corporate to the said company or Body Corporate ii) Central Tax, State Tax, Union territory Tax, Integrated Tax and Cess |
Statements and Documents
It shall be necessary for the registered person to submit to the proper officer the following Statements and Documents:
- A copy of the Audited Annual Accounts;
- Reconciliation Statement under Section 44(2) of the CGST Act/SGST Act e.
The aforesaid Reconciliation Statement shall be duly certified in FORM GSTR-9C, electronically through the common portal either directly or through a Facilitation Centre notified by the Commissioner.
- Other prescribed documents in the prescribed form and prescribed
It is also to be borne in mind that the Government is yet to prescribe the format of the Audit Report and Annexures thereto. Further, it is also not yet clear, whether auditor is required to identify and report the discrepancies month-wise or annually.
Appointment & Removal
Appointing Authority of GST Auditor
- In case of a company the appointment of the GST auditor shall be made by a resolution of the Board of Directors or by an officer of the company, if so authorized by the Board in this
- In case of a partnership firm or proprietary concern, the appointment can be made by a partner or the proprietor or a person authorized by the assessee. The acceptance of appointment by the proposed GST Auditor shall also be communicated in writing to the
Removal of GST Auditor
- Any resolution to remove a statutory auditor shall not be effective unless there are good and substantial grounds for the removal related to the conduct of the auditor with regard to the performance of his or her duties as auditor. However, the auditor cannot be removed on the ground that he has given an adverse or qualified Audit
- In the event an auditor has been removed without any valid grounds, the Ethical Standards Board of ICAI or ICWAI, as the case may be, can intervene and it may direct the incoming auditor not to accept the audit
GST has been implemented with effect from 01.07.2017. As a consequence, during the financial year 2017-18, GST remained in force only for a period of nine months from 01.07.2017 to 31.03.2018.
 |
The point of consideration is whether the above-mentioned annual turnover limit of Rs. 2 crore for audit purposes shall apply proportionately in the given case for a period of nine months or whether the foregoing limit shall apply as it is for a period of nine months ? |
A suitable and immediate clarification from the Government(s) is required in this regard. However, considering the old laws and the interpretation thereof the aggregate turnover shall be considered for the nine months only
It can be inferred that only for the purpose of determining the eligibility of the assessee who is required to get its accounts audited by a Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant, the all India based turnover shall be considered.
 |
The turnover limit of Rs. 2 Crore shall be computed by including turnover in all the States or Union territories, as the case may be, i.e. on all India basis under same PAN
Furthermore, the foregoing threshold turnover limit of Rs. 2 Crore is same for assessee’s in all the States and Union Territories Thus, it can be safely inferred that no separate threshold limit has been specified for Special Category States. Since each of the State GST Acts also has the provisions relating to GST Audit, it appears that the GST audit shall be conducted state-wise |

